N95 masks are essential personal protective equipment (PPE) widely used in healthcare settings and by the general public for protection against airborne particles and contaminants. While many are familiar with the N95 mask, the materials and structural composition often remain a mystery to many. As a nonwoven fabric manufacturer and mask materials supplier, we aim to provide a clear understanding of what goes into an N95 mask and how each material plays a role in ensuring its effectiveness.
Types of N95 Masks
Before diving into the material details, it’s important to note that N95 masks are defined by their filtration efficiency: they are capable of filtering out at least 95% of airborne particles, including those that are as small as 0.3 microns. There are various types of N95 masks, such as those with or without a valve, but the core structure remains similar.
Structural Analysis of an N95 Mask
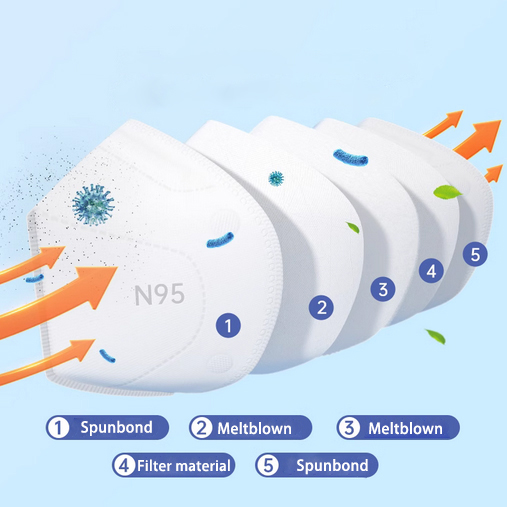
An N95 mask is constructed using a combination of nonwoven fabrics and other materials that provide high-efficiency filtration, comfort, and a secure fit. The layers of a typical N95 mask include the outer layer, middle filtration layer, and inner layer. Here’s a breakdown of the materials used in each layer:
1. Outer Layer: Spunbond Nonwoven Fabric
The outermost layer of an N95 mask is typically made from polypropylene spunbond nonwoven fabric, This layer serves several functions:
- Barrier Protection: It helps protect the mask from external contaminants, such as dust, droplets, and other large particles.
- Durability: Spunbond fabrics provide structural integrity to the mask, ensuring it holds its shape during wear.
- Breathability: Spunbond material is lightweight and breathable, providing comfort to the wearer without compromising safety.
2. Middle Layer: Meltblown Nonwoven Fabric
The most critical layer in an N95 mask for filtration is the N95 meltblown nonwoven fabric. This layer is composed of very fine polypropylene fibers that are electrostatically charged, allowing them to trap and filter out tiny airborne particles, including viruses and bacteria. Key features of this layer include:
- Filtration Efficiency: The meltblown fabric is designed to filter out at least 95% of particles, including those as small as 0.3 microns, making it essential for the mask’s high level of protection.
- Electrostatic Charge: The electrostatic charge in the meltblown layer increases its ability to capture small particles, improving the mask’s overall effectiveness.
- Breathability vs. Protection: While this layer provides exceptional filtration, it is also designed to maintain breathability, allowing for comfortable extended wear.
3. Inner Layer: Spunbond Nonwoven Fabric
The inner layer of the N95 mask is typically another spunbond nonwoven fabric, similar to the outer layer but with a focus on comfort and skin protection. The inner layer serves to:
- Comfort: The inner layer is designed to be soft against the skin, reducing irritation during prolonged use.
- Moisture Absorption: This layer helps absorb moisture from the wearer’s breath, preventing the mask from becoming damp and uncomfortable.
- Breathability: Just like the outer spunbond layer, the inner layer is lightweight and breathable, which helps the wearer feel more comfortable.
4. Nose Bridge Strip
In addition to the fabric layers, the Nose Bridge Strip plays a crucial role in ensuring a secure fit. Typically made from metal or plastic material, the nosepiece is covered with a soft foam pad for comfort. It helps the mask mold to the shape of the wearer’s nose, providing a tight seal to prevent leaks and improve filtration efficiency.
5. Ear Loops or Headbands
The ear loops or headbands are made from elastic material, such as spandex or latex, which helps secure the mask to the wearer’s face. These components are adjustable to ensure a snug fit, which is essential for maintaining the mask’s protective capabilities.
Material Composition Breakdown
Here’s a quick summary of the materials used in an N95 mask:
| Layer | Material | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Outer Layer | Spunbond Nonwoven Fabric (Polypropylene) | Barrier protection and structural integrity |
| Middle Layer | Meltblown Nonwoven Fabric (Polypropylene) | High-efficiency filtration of airborne particles |
| Inner Layer | Spunbond Nonwoven Fabric (Polypropylene) | Comfort, moisture absorption, and breathability |
| Nosepiece | Metal/Plastic with Foam Padding | Molds to the nose for a tight seal |
| Ear Loops/Headbands | Elastic Material (Spandex/latex) | Secures the mask to the face for a snug fit |
Conclusion
Understanding the materials and structure of an N95 mask is essential for manufacturers, suppliers, and buyers alike. Each layer of the mask serves a specific purpose, from ensuring high filtration efficiency to providing comfort and a secure fit. As a leading nonwoven fabric manufacturer and mask materials supplier, we are committed to delivering high-quality materials that contribute to the production of reliable, effective protective masks.
By choosing the right materials, manufacturers can ensure that their N95 masks provide the maximum protection while maintaining comfort for the wearer. Whether you are a mask manufacturer or a materials purchaser, knowing the science behind N95 masks will help you make informed decisions for your business.
