Isolation gowns and surgical gowns serve distinct purposes in healthcare settings, particularly for infection control, and their differences lie in their design, material, and intended use.this article we will talk about the difference between surgical gown and isolation gown.
What Is Isolation Gown?
Isolation gowns serve as PPE designed to protect the wearer from potential infection. They prevent healthcare professionals from coming into contact with contaminants and help reduce the risk of transferring harmful microorganisms to vulnerable patients. Isolation gowns are a standard choice for use in hospitals, clinics, emergency rooms, and nursing homes, providing a barrier to minimize exposure to bacteria and fluids.
Typically, isolation gowns are made of lightweight, disposable materials like non-woven fabrics and are used in situations where there is a moderate risk of contamination. They are generally less protective than surgical gowns but are versatile for a range of healthcare settings.
What Is Surgical Gown?
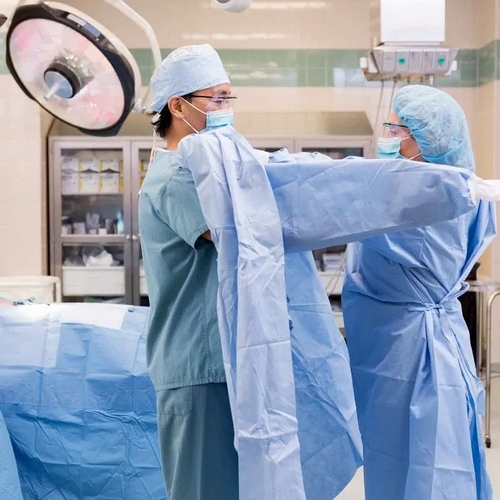
Surgical gowns are specifically designed for use during surgical procedures to protect both the patient and medical personnel from microbial contamination, blood, and body fluids. Made from higher-quality, durable materials, surgical gowns are crafted to endure the demands of the operating room. These gowns provide a more robust barrier against fluids and infectious agents and are often worn during invasive procedures.
Unlike isolation gowns, surgical gowns maintain sterility and are essential in procedures that require a sterile environment to prevent infections. Some designs feature additional protective layers in critical areas, like the chest and sleeves, for enhanced safety.
Differences in Materials
The materials used for isolation gowns and surgical gowns vary to suit their respective environments:
what material are isolation gowns made of?
Isolation Gowns: Typically made from lightweight and breathable materials such as PP (Polypropylene), PP+PE (Polyethylene), or SMS (Spunbond Meltblown Spunbond) fabrics, allowing comfort during extended wear. These materials provide moderate resistance to fluid penetration and are often chosen for short-term use in less critical settings.
what material are surgical gowns made of?
Surgical Gowns Generally made from more advanced materials like SMS, SMMS (Spunbond Meltblown Meltblown Spunbond), or SMMMS, offering higher resistance to fluids and microbial penetration. These materials are designed to maintain a sterile barrier, especially in the gown’s critical zones (areas in direct contact with fluids or infectious materials).
Styles and Design Variations
The styles of isolation and surgical gowns reflect their functional differences:
- Isolation Gowns: These gowns are typically loose-fitting with elastic or knitted cuffs and may feature Velcro or tie closures around the neck. The design allows for easy donning and removal, which is important in situations where gowns may be changed frequently.
- Surgical Gowns: These gowns feature a more fitted design with long sleeves, secure closures, and reinforced seams. The front chest and sleeves may be enhanced with additional protective layers like PP+PE for improved fluid resistance. The use of ultrasonic welding in seams ensures a secure barrier against contaminants.
Color Differences
The color of surgical and isolation gowns is often determined by the specific medical setting:
- Surgical Gowns: Commonly blue or green, as these colors provide a contrast to red, helping to reduce eye strain during surgical procedures. The blue tone is specifically chosen because it helps surgeons maintain focus and clarity during operations.
- Isolation Gowns: Available in a wider range of colors, including blue, yellow, and pink, depending on the healthcare setting. For example, yellow is often used in general hospital settings due to its high visibility, while pink may be chosen in pediatrics to create a more calming environment for young patients.
Quality Standards of Protection
Both surgical and isolation gowns are categorized based on their levels of protection:
- Level 1: Provides basic protection suitable for low-risk situations, such as administering injections or routine patient care.
- Level 2: Offers moderate protection, ideal for procedures like catheter insertion where the risk of contamination is higher.
- Level 3: Ensures high-level protection for high-risk situations, such as surgeries or labor and delivery, where the risk of fluid exposure is significant.
Surgical gowns typically undergo more rigorous testing for fluid resistance and microbial barrier properties to ensure a sterile environment is maintained throughout use.
